LLM-driven querying
I deployed a Streamlit-based “Natural-Language → SPARQL Workbench” connected to Gemini 2.5 Flash, enabling free-text queries over the integrated knowledge graph.
A single carefully designed SYSTEM prompt constrains the LLM to the exact graph schema, named graphs, and query patterns, allowing it to translate natural-language questions into valid, performant SPARQL rather than open-ended text generation.
Stack in one glance
- IaaS : Google Cloud VM
- Triple store : GraphDB
- LLM : Gemini 2.5 Flash (API)
- UI : Streamlit
SYSTEM prompt (excerpt)
Prompt
You are a SPARQL generator for a GraphDB endpoint.
1 NAMED GRAPHS
<http://bio.gtex> – GTEx normal tissue (heart, kidney, lung, breast) …
<http://bio.tcga> – TCGA tumor expression …
<http://bio.kinase> – ChEMBL kinase slice …
<http://bio.uniprot2ensembl> – UniProt ↔ Ensembl mapping …
3 TISSUE IRIs
Heart UBERON_0000948 | Kidney UBERON_0002113 | Lung UBERON_0002048 | Breast UBERON_0000310
5 EXPRESSION / SAMPLE PATTERN
?expr sio:has_value ?v ; sio:isAbout ?gene ; sio:isPartOf ?sample .
?sample sio:isAbout <UBERON tissue IRI> .
8 STYLE & PERFORMANCE RULES
1. Start with the tissue filter.
2. Use VALUES/FILTER IN for multi-tissue.
3. Avoid DISTINCT unless asked; always LIMIT.
Examples
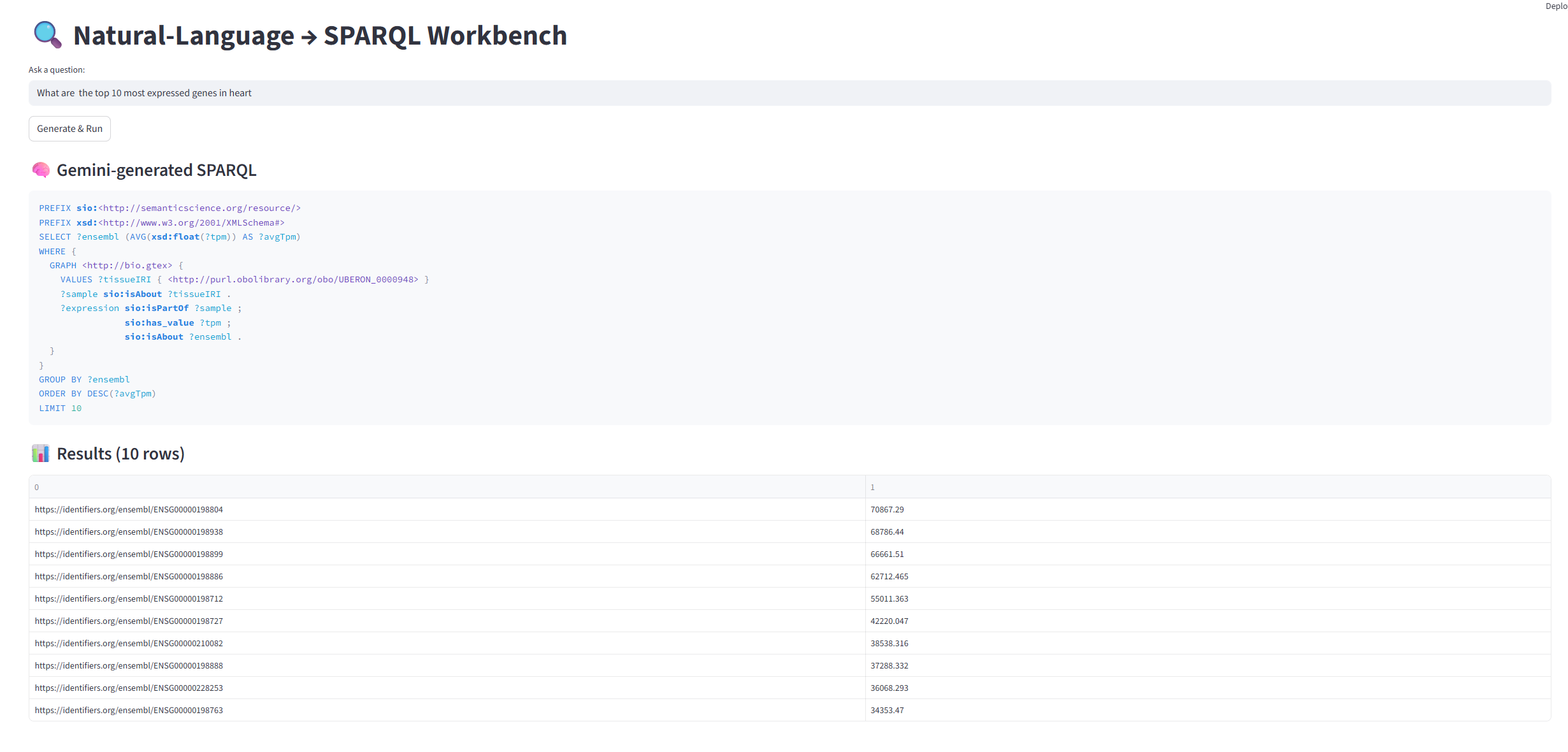
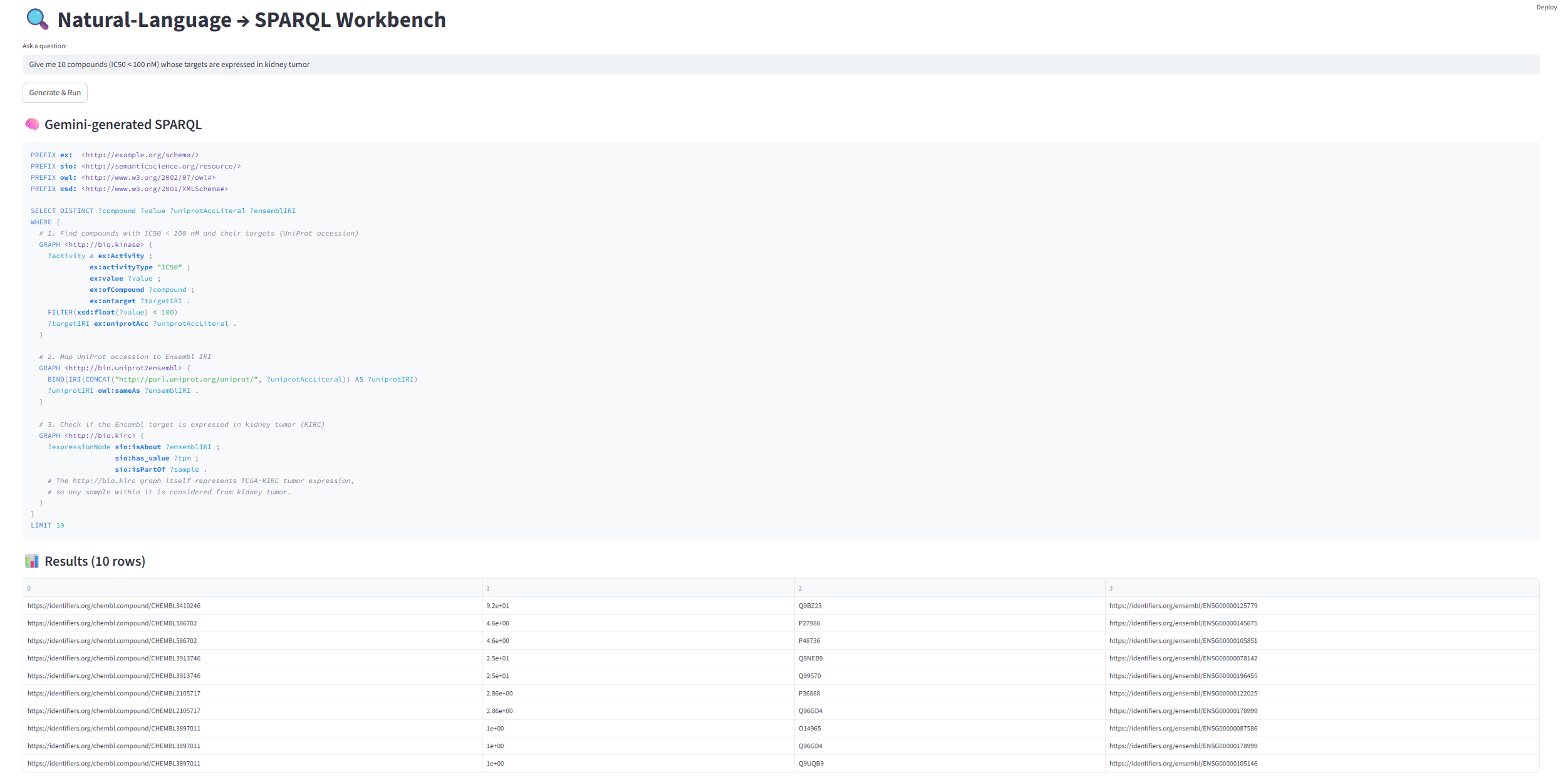
These examples demonstrate how the integrated knowledge graph can be queried to connect compound bioactivity, kinase targets, and tissue-specific gene expression across curated biomedical datasets.
Rather than relying on isolated tables or flat files, semantic integration enables biologically meaningful questions to be expressed directly at the data layer.
'What are the top 10 most expressed genes in heart'
'Give me 30 compounds (IC50 < 100 nM) whose targets are expressed in kidney tumor)'
These examples illustrate how semantic integration enables cross-domain biological questions that would be difficult to express using isolated datasets.
When paired with LLM-assisted querying, the knowledge graph supports rapid hypothesis generation, exploratory target prioritization, and transparent, reproducible analytics, while retaining full control over the underlying data model and query logic.